Genetic Variation: Overview and Examples
- 17th March 2023
- Posted by: Breige McBride
- Categories: Genetic Variation, Uncategorised
Whether you are looking for a genetic variation analysis service, or just want to know what genetic variation is, we can help. Read on to learn more!
What is genetic variation?
Genetic variation is what makes individuals of the same species different from each other. It refers to the differences in the DNA sequences of members of the same species. For example, in humans, it is the cause of our differences in terms of hair colour, blood type, and face shape and even determines whether or not we have dimples.
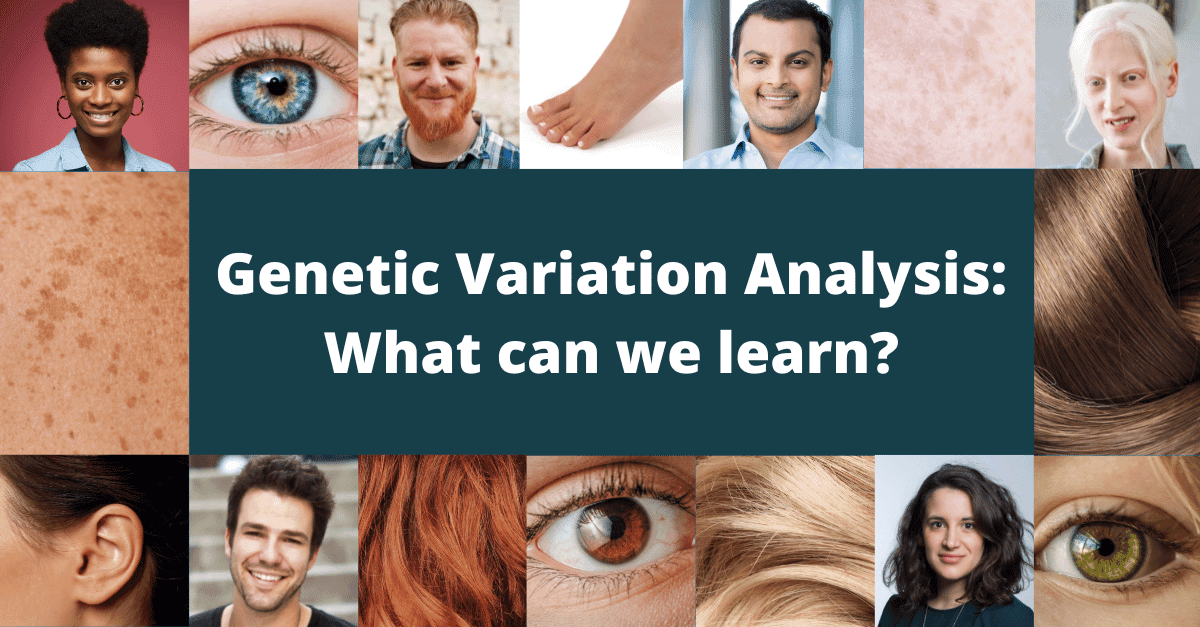
Genetic variation occurs in all the cells of an organism, but only the variations which occur in germ cells (cells which become reproductive cells – i.e. sperm and eggs) can be inherited, or passed down through generations. In fact, the variations which occur over generations can ultimately impact evolution.
What are the types of genetic variation?
There are 4 types or causes of genetic variation. These are:
- Mutation
- Recombination
- Random mating
- Random fertilisation
Examples of genetic variation
Genetic variation examples differ between species. For instance, examples in humans include:
- Eye colour
- Blood type
- Albinism
- Skin colour
- Toe length
- Face shape
- Dimples
- Attached or unattached ear lobes
- Ear hair growth
- Photic sneeze reflex (bright lights triggering sneezing)
Meanwhile, examples in cats include:
- Size
- Coat colour/markings
- Eye colour
- Hair length (long or short-haired)
When does genetic variation occur?
The time when genetic variation occurs in an organism depends on the type of variation occurring. Some variations only occur at the beginning of an organism’s development, while others may occur throughout its lifetime.
Variations caused by mutation, for example, can be inherited from parents, or they can be acquired later in life from another source, e.g. due to ultraviolet radiation from the sun. For this reason, mutations can be categorised as ‘inherited’ (passed from the parents) or ‘somatic’ (changes to DNA, which happen after conception and do not affect the germ cells (sperm or egg cells) so cannot be passed to offspring).
On the other hand, genetic variants caused by recombination only occur during an organism’s development. In simple terms, recombination refers to the mixing of the mother’s and father’s DNA in order to create new combinations of variants in offspring.
What is genetic variation analysis?
Genetic variation analysis, or genetic variant analysis, is the process of investigating genetic variations and their associations with clinical outcomes. For example, this type of analysis can reveal links between genetic variants and medical conditions.
Genetic variation analysis from Fios Genomics
As a bioinformatics analysis company which works with pharma and biotech companies to further drug development research, we have a wealth of experience in genetic variation data analysis. From using whole exome or whole genome sequencing analysis (WES or WGS) or SNP arrays to profile genetic variation across many loci in the genome simultaneously, to using GWAS* or pheWAS** to investigate links between SNPs and diseases like heart disease or cancer, there are many ways we can support your drug development research with genetic variation analysis. To discover how we can support your particular research, contact us today! Alternatively, learn more about our genetic variation data analysis services.
(P.S. Never outsourced bioinformatics before? Don’t worry, because you can learn everything you need to know in our Bioinformatics Buyer’s Guide. The guide contains information on everything from the stages of your project that a bioinformatics provider can assist with; as well as what you should consider if you plan to publish your research in high-impact journals. It also includes a handy check-list of questions you can ask providers to ensure you work with the one that will best meet your needs. Get the guide now!)
Author: Breige McBride, Content and Social Media Manager, Fios Genomics
Reviewed by Fios Genomics Bioinformatics Experts to ensure accuracy
Further Reading
What is a gene variant and how do variants occur?
How are gene variants involved in evolution?
See Also:
The Future of Bioinformatics in 2023
The Clinical Trial Diversity Problem
Bioinformatics and the Pharmaceutical Industry
How to Reduce Animal Testing With Bioinformatics
Plant Metabolomics Analysis: Revealing Plants Secrets
*GWAS refers to a genome-wide association study.
**pheWas refers to Phenome-wide association studies.
Download our Analysis Reports for GWAS Data
Fill in the form below to access the data analysis report our team created. In the report, bioinformatics analysis of publicly available genetic datasets from the International HapMap Project and a simulated binary phenotype, helped to identify genetic loci associated with the binary phenotype and annotate the loci with associated genes.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.